This Version
Latest Version
Previous Version
- This is the first version.
Authors
Contributors
Table of Contents
Contents
Resource Properties
Performance Monitoring Service Provider Capabilities
Service Discovery and Description
Resource Shapes
Service Provider Resource
Creation Factories
Query Capabilities
Delegated UIs
Service Provider HTTP Method Support
Performance Monitoring Specification Guidelines
Appendix A: Samples
Appendix B: Resource Shapes
Appendix C: Notices and References
Notation and Conventions
The key words “MUST”, “MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”, “SHALL”, “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD NOT”, “RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL” in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC2119. Domain name examples use RFC2606.
Introduction
(this section is informative)
This specification builds on the OSLC Core Specification to define the resources and operations supported by an Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration (OSLC) Performance Monitoring provider. This version of the specification has version 2.0 to indicate that it is an OSLC Core 2.0 compliant specification.
Performance Monitoring resources define records whose content is most useful in the testing and operational stages of the software development, test, and deployment lifecycle. They represent individual resources as well as their relationships to other resources and to other linked resources outside of the Performance Monitoring domain. The intent of this specification is to define the set of HTTP-based RESTful interfaces in terms of HTTP methods: GET, POST, PUT and DELETE, HTTP response codes, MIME type handling and resource formats. The capabilities of the interface definitions are driven by key integration scenarios and therefore do not represent a complete set of operations on resources or resource types. The resource formats and operations may not exactly match the native models supported by existing implementations, but are intended to be compatible with them.
Performance Monitoring, as referenced in this specification, refers to the collection of data about Information Technology (IT) systems such as servers, workstations, services, and transactions to assess their operational health and enable proactive manual human intervention before emerging problems escalate into widespread degradation or outages. See the Performance Monitoring Scenarios page for several specific examples.
Terminology
Service Provider - an implementation of the OSLC Performance Monitoring specification as a server. OSLC Performance Monitoring clients consume these services.
Performance Monitoring Record - Defines the unit of information made available by a Performance Monitoring service provider. The information could be numeric metrics, status, or some other kind of property of interest to monitoring consumers.
Monitored resource - An entity such as a software server or computer system that is monitored by a software agent to ensure its performance and availability. In this specification when we use the word ‘resource’ to mean a monitored resource rather than an OSLC resource, we try to qualify the word to make our intent clear.
Base Requirements
Compliance
This specification is based on OSLC Core Specification. OSLC Performance Monitoring consumers and service providers MUST be compliant with both the core specification and this Performance Monitoring specification, and SHOULD follow all the guidelines and recommendations in both these specifications.
The following table summarizes the requirements from OSLC Core Specification as well as some (but not all) additional requirements specific to Performance Monitoring. See the full content of the Performance Monitoring specification for all requirements. Note that this specification further restricts some of the requirements for OSLC Core Specification as noted in the Origin column of the compliance table. See further sections in this specification or the OSLC Core Specification to get further details on each of these requirements.
Any consumer or service provider behaviors are allowed unless explicitly prohibited by this or dependent specifications; conditional permissive requirements, especially those qualified with “MAY”, are implicitly covered by the preceding clause. While technically redundant in light of that broad permission, OSLC specifications do still make explicit MAY-qualified statements in cases where the editors believe doing so is likely to add clarity.
Requirements on OSLC Consumers
| Requirement |
Level |
Origin(s) |
Meaning |
| Unknown properties and content |
MUST |
Core |
OSLC clients MUST preserve unknown content |
Requirements on OSLC Service Providers
| Requirement |
Level |
Origin(s) |
Meaning |
| Unknown properties and content |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC service providers MAY ignore unknown content |
| Unknown properties and content |
MUST |
Core |
OSLC service providers MUST return an error code if recognized content is invalid. |
| Resource Operations |
MUST |
Core |
OSLC service providers MUST support resource operations via standard HTTP operations |
| Resource Paging |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC services MAY provide paging for resources |
| Partial Resource Representations |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC service providers MAY support HTTP GET requests for retrieval of a subset of a resource’s properties via the oslc.properties URL parameter |
| Partial Resource Representations |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC service providers MAY support HTTP PUT requests for updating a subset of a resource’s properties via the oslc.properties URL parameter |
| Service Provider Resources |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC service providers MAY provide a Service Provider Catalog resource |
| Service Provider Resources |
MUST |
Core |
OSLC service providers MUST provide a Service Provider resource |
| Creation Factories |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC service providers MAY provide creation factories to enable resource creation via HTTP POST |
| Query Capabilities |
SHOULD1 |
Perf Mon, Core |
OSLC service providers SHOULD provide query capabilities to enable clients to query for resources |
| Query Syntax |
MUST2 |
Perf Mon, Core |
If a service provider supports a OSLC query capability, its query capabilities MUST support the OSLC Core Query Syntax |
| Delegated UI Dialogs |
SHOULD |
Core |
OSLC service providers SHOULD allow clients to discover, via their service provider resources, any Delegated UI Dialogs they offer. |
| Delegated UI Dialogs |
SHOULD |
Core |
OSLC service providers SHOULD offer delegated UI dialogs for resource creation |
| Delegated UI Dialogs |
SHOULD |
Core |
OSLC service providers SHOULD offer delegated UI dialogs for resource selection |
| UI Preview |
SHOULD |
Core |
OSLC Services SHOULD offer UI previews for resources that may be referenced by other resources |
| HTTP Basic Authentication |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC Services MAY support Basic Auth |
| HTTP Basic Authentication |
SHOULD |
Core |
OSLC Services SHOULD support Basic Auth only over HTTPS |
| OAuth Authentication |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC service providers MAY support OAuth |
| OAuth Authentication |
SHOULD |
Core |
OSLC service providers that support OAuth SHOULD allow clients to discover the required OAuth URLs via their service provider resource |
| Error Responses |
MAY |
Core |
OSLC service providers MAY provide error responses using Core-defined error formats |
| RDF/XML Representations |
MUST3 |
Perf Mon, Core |
OSLC service providers MUST offer an RDF/XML representation for HTTP GET responses |
| RDF/XML Representations |
MUST3 |
Perf Mon, Core |
OSLC service providers MUST accept RDF/XML representations on PUT requests. |
| RDF/XML Representations |
MUST3 |
Perf Mon, Core |
RDF/XML representations on POST requests whose semantic intent is to create a new resource instance. |
| XML Representations |
MAY3 |
Perf Mon, Core |
OSLC service providers MAY provide a XML representation for HTTP GET, POST and PUT requests that conform to the Core Guidelines for XML. |
| JSON Representations |
MAY3 |
Perf Mon, Core |
OSLC service providers MAY provide JSON representations for HTTP GET, POST and PUT requests that conform to the Core Guidelines for JSON |
| HTML Representations |
SHOULD3 |
Perf Mon, Core |
OSLC service providers SHOULD provide HTML representations for HTTP GET requests |
- 1The OSLC Core Specification indicates service providers MAY provide Query Capabilities. This specification strengthens the requirement.
- 2The OSLC Core Specification indicates service providers MAY support the OSLC Query Syntax. This specification makes OSLC Query Syntax support a MUST requirement for service providers providing query capabilities.
- 3Support for all common HTTP methods is not required for all resources defined by this specification. See the HTTP Method support table for details.
Specification Versioning
See OSLC Core Specification Versioning section.
Namespaces
Defined
OSLC Performance Monitoring defines the namespace shown in the table below. This namespace URI and prefix are used to designate the resources and their properties defined in this specification.
Use of the suggested prefix is RECOMMENDED, because doing so aids debugging and other situations where humans read the data.
| Suggested namespace prefix |
Namespace URI |
pm |
http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon# |
Re-used from other specifications
In addition to the namespace URIs and namespace prefixes defined in the OSLC Core specification, OSLC Performance Monitoring also re-uses vocabulary terms from other namespaces. The namespace prefixes in the table below are used in this specification, and match the recommendations made by the specification that defines each.
| Namespace prefix used |
Namespace URI |
Usage |
ems |
http://open-services.net/ns/ems# |
Vocabulary is required for Performance Monitoring providers to expose metrics. Defined in the OSLC Estimation and Measurement domain. |
crtv |
http://open-services.net/ns/crtv# |
Vocabulary is expected to be commonly used by Performance Monitoring providers, but is not required. Defined in the OSLC Reconciliation domain. |
In addition to the requirements for OSLC Defined Resource Representations, this section outlines further refinements and restrictions.
See HTTP Method support table for further clarification on support for HTTP methods and media types for each OSLC Performance Monitoring resource.
For HTTP GET requests on all OSLC Performance Monitoring and OSLC Core defined resource types,
- Performance Monitoring Providers MUST provide RDF/XML representations. If provided, the RDF/XML representation SHOULD follow the guidelines outlined in the OSLC Core Representations Guidance for RDF/XML.
- Performance Monitoring Providers MAY provide XML and JSON representations. The XML and JSON representations SHOULD follow the guidelines outlined in the OSLC Core Representations Guidance.
- Performance Monitoring Consumers requesting RDF/XML SHOULD be prepared for any valid RDF/XML document. Performance Monitoring Consumers requesting XML SHOULD be prepared for representations that follow the guidelines outlined in the OSLC Core Representations Guidance.
- Performance Monitoring Providers SHOULD support an [X]HTML representation and a user interface (UI) preview as defined by UI Preview Guidance
For HTTP PUT/POST request formats for Performance Monitoring resources,
- Performance Monitoring Providers MUST accept RDF/XML representations and MAY accept XML representations. Performance Monitoring Providers accepting RDF/XML SHOULD be prepared for any valid RDF/XML document. If XML is accepted, Performance Monitoring Providers SHOULD be prepared for representations that follow the guidelines outlined in the OSLC Core Representations Guidance.
- Performance Monitoring Providers MAY accept XML and JSON representations. Performance Monitoring Providers accepting XML or JSON SHOULD be prepared for representations that follow the guidelines outlined in the OSLC Core Representations Guidance.
For HTTP GET response formats for Query requests,
- Performance Monitoring Providers MUST provide RDF/XML and MAY provide JSON, XML, and Atom Syndication Format XML.
When Performance Monitoring Consumers request:
application/rdf+xml Performance Monitoring Providers MUST respond with RDF/XML representation without restrictions.application/xml Performance Monitoring Providers SHOULD respond with OSLC-defined abbreviated XML representation as defined in the OSLC Core Representations Guidanceapplication/atom+xml Performance Monitoring Providers SHOULD respond with Atom Syndication Format XML representation as defined in the OSLC Core Representations Guidance- If supported, the Atom Syndication Format XML representation SHOULD use RDF/XML representation without restrictions for the atom:content entries representing the resource representations.
Authentication
See OSLC Core Authentication section. This specification puts no additional constraints on authentication.
Error Responses
See OSLC Core Error Responses section. This specification puts no additional constraints on error responses.
Performance Monitoring Providers SHOULD support pagination of query results and MAY support pagination of a single resource’s properties as defined by the OSLC Core Specification.
Labels for Relationships
Relationships to other resources are represented as properties whose values are the URI of the object or target resource. When a relationship property is to be presented in a user interface, it may be helpful to provide an informative and useful textual label for that relationship instance. (This in addition to the relationship property URI and the object resource URI, which are also candidates for presentation to a user.) OSLC Core Links Guidance allows OSLC providers to support a dcterms:title link property in resource representations, using the anchor approach (reification), but this specification discourages its use (providers SHOULD NOT use it, and consumers SHOULD NOT depend on it). At the time this specification was written, the W3C RDF working group was on a path to remove reification from the next version of RDF, and it was noted that reification never was normatively defined even in the RDF/XML syntax W3C Recommendation, where it occurs informatively.
Resource Definitions
A list of properties is defined for each type of resource. Most of these properties are identified in OSLC Core Appendix A: Common Properties. Any exceptions are noted. Relationship properties refer to other resources. These resources MAY be any resource; that is, they MAY or MAY NOT be in any OSLC domain, including Performance Monitoring. Likewise, they MAY or MAY NOT be HTTP or RDF resources.
The diagram below shows an example of one way that a Performance Monitoring Record resource may relate to the resources it describes. With this option, the Performance Monitoring record uses the isPartOf predicate to refer to the monitored resource its describing.
Another option is described near the bottom of this specification in the section entitled Performance Monitoring Specification Guidelines.
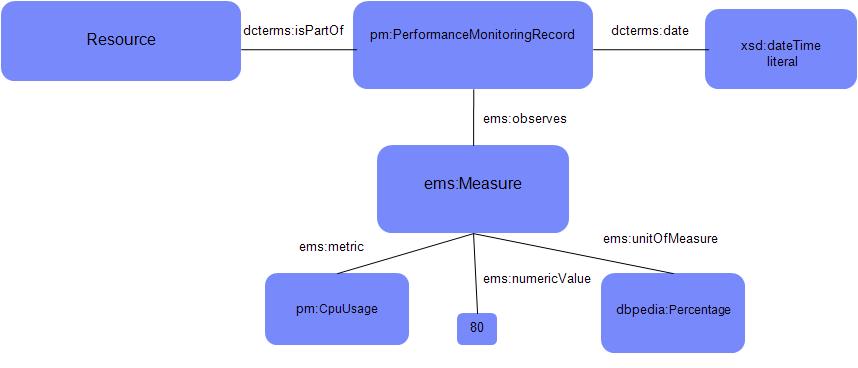
For all resource types defined in this specification, all required properties (those defined with an occurrence of exactly-one or one-or-many) MUST exist for each resource and MUST be provided when requested. All other properties are optional, and might not exist on some or any resources; those that do not exist will not be present in the returned representation even if requested, while those that do exist MUST be provided if requested. Providers MAY define additional provider-specific properties; providers SHOULD use their own namespaces for such properties, or use standard Dublin Core or RDF namespaces and properties where appropriate.
If no specific set of properties is requested, all properties are returned - both those defined in this specification as well as any provider-specific ones. See Selective Property Values in the OSLC Core Specification.
- Name:
PerformanceMonitoringRecord
- Description: A resource representing performance monitoring information. This could be numeric metrics, status, or some other kind of property of interest to monitoring consumers.
- Type URI
http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#PerformanceMonitoringRecord
| Prefixed Name |
Occurs |
Read-only |
Value-type |
Representation |
Range |
Description |
| OSLC Core: Common Properties |
|
|
|
|
|
|
rdf:type |
zero-or-many |
unspecified |
Resource |
Reference |
n/a |
The resource type URIs (RDF). |
dcterms:title |
zero-or-one |
unspecified |
XMLLiteral |
n/a |
n/a |
A name given to the resource (reference: Dublin Core). The title of the resource represented as rich text in XHTML content. Its value SHOULD include only content that is valid inside an XHTML <span> element (OSLC Core - Common). |
dcterms:description |
zero-or-one |
unspecified |
XMLLiteral |
n/a |
n/a |
An account of the resource (Dublin Core). The value SHOULD be represented as rich text in XHTML syntax, and SHOULD include only content that is valid and suitable inside an XHTML <div> element (OSLC Core - Common). |
dcterms:identifier |
zero-or-one |
True |
String |
n/a |
n/a |
An unambiguous reference to the resource within a given context (Dublin Core). A unique identifier for a resource. Typically read-only and assigned by the service provider when a resource is created. Not typically intended for end-user display (OSLC Core - Common). |
dcterms:created |
zero-or-one |
True |
DateTime |
n/a |
n/a |
Timestamp of resource creation (Dublin Core) |
dcterms:modified |
zero-or-one |
True |
DateTime |
n/a |
n/a |
Date on which the resource was changed (Dublin Core). Timestamp of latest resource modification (OSLC Core - Common). |
oslc:instanceShape |
zero-or-one |
True |
Resource |
Reference |
oslc:ResourceShape |
A link to the resource’s OSLC Resource Shape that describes the possible properties, occurrence, value types, allowed values and labels. This shape information is useful in displaying the subject resource as well as guiding clients in performing modifications (OSLC Core - Common). |
oslc:serviceProvider |
zero-or-one |
True |
Resource |
Reference |
oslc:ServiceProvider |
A link to the resource’s OSLC Service Provider (OSLC Core - Common). |
| Prefixed Name |
Occurs |
Read-only |
Value-type |
Representation |
Range |
Description |
| OSLC Performance Monitoring: Start of additional properties |
|
|
|
|
|
|
dcterms:date |
zero-or-one |
True |
dateTime |
n/a |
n/a |
The time at which the record was collected (Dublin Core). Performance Monitoring service providers MUST provide an explicit time zone facet value (Performance Monitoring). This requirement is necessary to avoid differences in interpretation between servers and clients in different time zones; it is functionally equivalent to using the dateTimeStamp datatype from XML Schema 1.1, but avoids any side effects on SPARQL queries. |
ems:observes |
zero-or-many |
True |
Resource |
Either |
n/a |
Something observed and measured about a resource (EMS). The ems:observes object will typically be of type ems:Measure, but it MAY be of any type (Core), (Core Links). When the resource is of type ems:Measure, that resource SHOULD contain an ems:Metric predicate whose object is of class pm:Metric (either directly or indirectly). |
dcterms:isPartOf |
exactly-one |
True |
Resource |
Reference |
n/a |
A related resource in which the described resource is physically or logically included (Dublin Core). The related resource typically has one or more of the following types, although it MAY be of any type(s): crtv:Process, crtv:StorageVolume, crtv:ComputerSystem, crtv:SoftwareServer, crtv:Database, crtv:SoftwareModule, crtv:ResourcePool, foaf:Agent. |
Resource: ems:Measure
The OSLC Estimation and Measurement (EMS) domain defines ems:Measure. This specification re-uses it without modifications, aside from defining additional metric subclasses in the Performance Monitoring vocabulary. Performance Monitoring Record instances will generally re-use units of measure from EMS and other vocabularies such as QUDT and dbpedia.
An example instance, that conveys "Real Memory Utilization"=50% using Turtle syntax, might be:
@prefix pm: <http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#> .
@prefix oslc: <http://open-services.net/ns/core#> .
@prefix dcterms: <http://purl.org/dc/terms/> .
@prefix ems: <http://open-services.net/ns/ems#> .
@prefix dbp: <http://dbpedia.org/resource/>.
@base <http://perfmon-provider.example.org/> .
<rec001#realmemutil50>
a ems:Measure ; # rdf:type
dcterms:title "Real Memory Utilization" ;
ems:metric <pm:RealMemoryUsed> ;
ems:unitOfMeasure <dbp:Percentage> ;
ems:numericValue 50 ;
.
Equivalent RDF/XML for the preceding example:
<rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:rdfs="http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#"
xmlns:owl="http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl#"
xmlns:dcterms="http://purl.org/dc/terms/"
xmlns:rddl="http://www.rddl.org/"
xmlns:qudt="http://qudt.org/1.1/schema/qudt"
xmlns:pm="http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#"
xmlns:ems="http://open-services.net/ns/ems#">
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://perfmon-provider.example.org/rec001#realmemutil50">
<rdf:type rdf:resource="http://open-services.net/ns/ems#Measure" />
<dcterms:title>Real Memory Utilization</dcterms:title>
<ems:metric rdf:resource="pm:RealMemoryUsed" />
<ems:unitOfMeasure rdf:resource="dbp:Percentage" />
<ems:numericValue rdf:datatype="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#double">
50</ems:numericValue>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
Metric Categories
This specification introduces metric categories, which loosely correspond to the major headings on the EMS working groups Key Software Metrics page: size, schedule, effort, and quality, derived. As the EMS work shows, categorization itself is not unique to Performance Monitoring. As was done in EMS, the categories defined by this specification are exposed to consumers via RDF Schema subclass annotations in the vocabulary document; an example is shown later in this section.
Exposing each metric’s categorization in the vocabulary definition serves several purposes:
- Clients can query for a subset of all metrics exposed in the PerformanceMonitoringRecord without having to enumerate the members of the subset explicitly.
- Implementations and other specifications can define new metrics and categorize them, allowing clients unaware of the new metrics’ property names to introspect some information that might influence how they are presented in a user interface.
A summary of the inheritance tree for categories defined by this specification is shown below. This shows, for example, that pm:ResourceUsageMetrics is a subclass of pm:Metric. Please consult the vocabulary document for the authoritative set of relationships.
* `pm:Metric`
* `pm:CpuMetrics`
* `pm:DiskMetrics`
* `pm:MemoryMetrics`
* `pm:BufferPoolMetrics`
* `pm:NetworkMetrics`
* `pm:RequestMetrics`
* `pm:FailureMetrics`
* `pm:ResponseTimeMetrics`
* `pm:ResourceAvailabilityMetrics`
* `pm:ResourceUsageMetrics`
* `pm:ResourceExhaustionMetrics`
* `pm:ThreadPoolMetrics`
* `pm:VirtualizationMetrics`
As with RDF types, categories are additive and potentially multi-valued. In other words, a given metric may be a member of as many classes as are semantically sensible. The hierarchy summarized above is useful to reduce redundancy only. For example, if a given metric is defined to be in the category pm:FailureMetrics, then it is redundant (although technically permissible) to define it to be in the category pm:RequestMetrics as well. Specific metrics like pm:RealMemoryUsed are associated with metric categories via the vocabulary document for the namespace by annotating the rdfs:Class with rdfs:subClassOf; the following example shows how to categorize pm:RealMemoryUsed as a resource usage metric and as a memory metric.
In RDF/XML syntax:
<rdf:RDF xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:rdfs="http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#">
<rdfs:Class rdf:about="http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#RealMemoryUsed">
<rdfs:isDefinedBy rdf:resource="http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#" />
<rdfs:subClassOf rdf:resource="http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#ResourceUsageMetrics"/>
<rdfs:subClassOf rdf:resource="http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#MemoryMetrics"/>
<rdfs:label>RealMemoryUsed</rdfs:label>
<rdfs:comment>Real memory used.</rdfs:comment>
</rdfs:Class>
</rdf:RDF>
In Turtle syntax:
@prefix rdf: <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#> .
@prefix rdfs: <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#> .
@prefix pm: <http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#> .
<http://open-services.net/ns/perfmon#RealMemoryUsed> a rdfs:Class ;
rdfs:isDefinedBy pm: ;
rdfs:subClassOf pm:ResourceUsageMetrics , pm:MemoryMetrics ;
rdfs:label "RealMemoryUsed" ;
rdfs:comment "Real memory used." .
This is the set of RDFS Classes that are all of the following:
- sub-classes of
ems:Metric (directly or indirectly)
- serve to define categories of metrics
- are actually sub-classed in the current vocabulary by more specific metrics, like
pm:AvgJmsGetTime.
In other words, they are “leaf” RDFS Classes that group set of metrics. Leaf classes, like pm:AvgJmsGetTime, are defined exactly like the categories in the table, and could be used as metric categories themselves by other vocabularies or implementations that sub-class them.
Resource Properties
In addition to resource definitions, this specification defines properties below that can occur in any RDF resource. In the scenarios currently addressed, they are most commonly used with resources of types such as the following, but this list is exemplary, not limiting: crtv:Process, crtv:StorageVolume, crtv:ComputerSystem, crtv:SoftwareServer, crtv:Database, crtv:SoftwareModule, crtv:ResourcePool, foaf:Agent. Not all properties will be semantically sensible with all resource types.
| Prefixed Name |
Occurs |
Read-only |
Value-type |
Representation |
Range |
Description |
pm:process |
zero-or-many |
True |
Resource |
Either |
n/a |
A process running, for example, in a computer system. Typically refers to a resource with type crtv:Process, but it MAY refer to other resource types. |
pm:disk |
zero-or-many |
True |
Resource |
Either |
n/a |
A disk attached, for example, to a computer system. Typically refers to a resource with type crtv:StorageVolume, but it MAY refer to other resource types. |
pm:monitoringAgent |
zero-or-many |
True |
Resource |
Either |
n/a |
Software that monitors a resource’s availability, performance, capacity, or utilization. Typically refers to a resource with type foaf:Agent, but it MAY refer to other resource types. |
pm:mobilityEnabled |
zero-or-one |
True |
boolean |
Inline |
n/a |
An indication about whether the resource, for example a virtual computer system, can move about dynamically. |
pm:tableReorganizationNeeded |
zero-or-one |
True |
boolean |
Inline |
n/a |
Indicates whether a database’s tables need to be reorganized. |
pm:availabilityStatus |
zero-or-many |
True |
Resource |
Reference |
n/a |
An indication of availability. If any value is present, then at least one of them MUST be from the list of URIs defined below. Additional values MAY be present from other namespaces, e.g. to provide more detailed product-specific status. All values present SHOULD be semantically compatible. |
Availability Status Property Values
OSLC Performance Monitoring service providers can identify the availabilityStatus using references to property values in the OSLC Performance Monitoring vocabulary or to property values that are not in the Performance Monitoring vocabulary (i.e. in the service provider’s own vocabulary). It is expected that the availabilityStatus values will be URI references to property values, but inline resources defining the availabilityStatus property values are also valid.
The resource shape governs occurrence constraints within PM. They say 0:* pm:availabilityStatus.
Hence:
The property values for pm:availabilityStatus are:
Service Discovery and Description
Resource Shapes
Performance Monitoring service providers MAY support Resource Shapes as defined in OSLC Core Specification Appendix A
Service Provider Resource
Performance Monitoring service providers MUST provide a Service Provider Resource that can be retrieved at a implementation dependent URI.
Performance Monitoring service providers MAY provide a Service Provider Catalog Resource that can be retrieved at a implementation dependent URI.
Performance Monitoring service providers MUST provide a oslc:serviceProvider property for their defined resources that will be the URI to a Service Provider Resource.
Performance Monitoring service providers SHOULD expose resource types of type pm:PerformanceMonitoringRecord. Performance Monitoring service providers SHOULD include the type pm:PerformanceMonitoringRecord on all resources that contain performance monitoring information.
Creation Factories
If an OSLC Performance Monitoring service provider supports the creation of resources, there MUST be at least one Creation Factory entry in its Services definition.
See the HTTP Method support table for further clarification on support for HTTP methods and media types for each OSLC Performance Monitoring resource.
Query Capabilities
There SHOULD be at least one Query Capability entry in the Services definition.
The Query Capability MUST support the oslc.where parameter and SHOULD support the oslc.select parameter. If the oslc.where parameter is supported, then the oslc.prefix parameter MUST be supported.
If shape information is NOT present with the Query Capability, service providers SHOULD use the default properties defined in OSLC Core RDF/XML Examples to contain the result.
Delegated UIs
OSLC Performance Monitoring service providers support the selection and creation of Performance Monitoring resources as defined by Delegated UIs in OSLC Core.
Performance Monitoring providers support requirements for delegated UIs as follows:
| Performance Monitoring Resource |
Selection |
Creation |
| PerformanceMonitoringRecord |
SHOULD |
MAY |
Service Provider HTTP Method Support
Support for all HTTP methods in the compliance table is not required for all Performance Monitoring resources. The following table summarizes the requirements for each resource definition, HTTP method, and media type combination. A value of N/A means this specification does not impose any constraints on it.
| Resource |
RDF/XML |
XML |
JSON |
HTML |
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Performance Monitoring Record |
|
|
|
|
|
| GET |
MUST |
MAY |
SHOULD |
SHOULD |
MAY |
| PUT |
MAY |
MAY |
MAY |
N/A |
MAY |
| POST |
MAY |
MAY |
MAY |
N/A |
MAY |
| DELETE |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
Performance Monitoring service providers SHOULD support deletion of any resources for which they allow creation.
(this section is informative)
In addition to a Performance Monitoring Record having a predicate to refer to the monitored resource is is part of using pm:isPartOf, a Performance Monitoring record may be a class type for a monitored resource, such that the pm:isPartOf predicate value refers to itself as the object value.
Extending Metrics
- Choose the correct metric categor(ies) for your metric.
- Decide whether your class should be part of the ‘perfmon’ namespace or a private namespace.
- Create an RDFS class for your metric.
- Create an instance of a PerformanceMonitoringRecord
- Put a timestamp on it to indicate when it was collected
- Put an ems:observes predicate in your PerformanceMonitoringRecord and have it refer to an ems:Measure instance
- Use your metric in the ems:Measure instance
- Use ems:unitOfMeasure to specify whether the metric is a rate, a ratio, a quantity, a time, etc.
- Relate PerformanceMonitoringRecord to monitored resource using isPartOf property
Appendix A: Samples
(this section is informative)
See OSLC Performance Monitoring 2.0 Appendix A: Samples
Appendix B: Resource Shapes
(this section is informative)
See OSLC Performance Monitoring 2.0 Appendix B: Resource Shapes
Appendix C: Notices and References
Contributors
Janet Andersen,
Jim Conallen,
John Arwe,
Julie Bielski,
Michael Fiedler,
Steve Speicher,
Tuan Dang
Reporting Issues on the Specification
The working group participants who author and maintain this working draft specification, monitor a distribution list where issues or questions can be raised, see Performance Monitoring Mailing List
Also the issues found with this specification and their resolution can be found at OSLC Performance Monitoring 2.0 Issues.
License and Intellectual Property
We make this specification available under the terms and conditions set forth in the site Terms of Use, IP Policy, and the Workgroup Participation Agreement for this Workgroup.
References





